Lysosomes
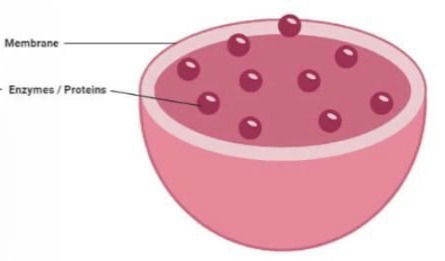
Lysosomes: are acidic, hydrolase-rich vacuoles capable of degrading most biological macromolecules. In spite of this digestive capacity, the acid hydro lases and associated proteins found in the lysosome's interior, as well as the proteins that comprise the lysosome membrane, are relatively long-lived. Nevertheless endogenous lysosomal constituents do turn over and are continuously replaced with newly synthesized components.
